Which of the following operations is not O(1) for an array of sorted data. You may assume that array elements are distinct?
Let A[1…n] be an array of n distinct numbers. If i < j and A[i] > A[j], then the pair (i, j) is called an inversion of A. What is the expected number of inversions in any permutation on n elements?
What are the disadvantages of arrays?
The following function reverse() is supposed to reverse a singly linked list. There is one line missing at the end of the function.
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* next;
};
static void reverse(struct node** head_ref)
{
struct node* pre = NULL;
struct node* curr = *head_ref;
struct node* next;
while (current != NULL)
{
next = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
/*ADD A STATEMENT HERE*/
}
What should be added in place of “/*ADD A STATEMENT HERE*/”, so that the function correctly reverses a linked list.
Consider the following pseudo code. Assume that IntQueue is an integer queue. What does the function fun do?
void fun(int n)
{
IntQueue q = new IntQueue();
q.enqueue(0);
q.enqueue(1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int a = q.dequeue();
int b = q.dequeue();
q.enqueue(b);
q.enqueue(a + b);
ptint(a);
}
}
Which of the following applications may use a stack?
What does ‘stack underflow’ refer to?
void fun(int n)
{
Stack S;
while (n > 0)
{
push(&S, n%2);
n = n/2;
}
while (!isEmpty(&S))
printf("%d ", pop(&S));
}
What does the above function do?
Consider the following pseudocode that uses a stack
declare a stack of characters
while ( there are more characters in the word to read )
{
read a character
push the character on the stack
}
while ( the stack is not empty )
{
pop a character off the stack
write the character to the screen
}
What is output for input “XYZ”?
A single array A[1..MAXSIZE] is used to implement two stacks. The two stacks grow from opposite ends of the array. Variables top1 and top2 (topl< top 2) point to the location of the topmost element in each of the stacks. If the space is to be used efficiently, the condition for “stack full” is
What is a full Binary tree?
The number of edges from the root to the node is called _____ of the tree.
Special node in tree structure which has many children and no parent node is called.
Consider a B+ tree in which the maximum number of keys in a node is 5. What is the minimum number of keys in any non-root node?
Which algorithm is used to compute minimum spanning tree
Non leaf nodes of tree structure form a
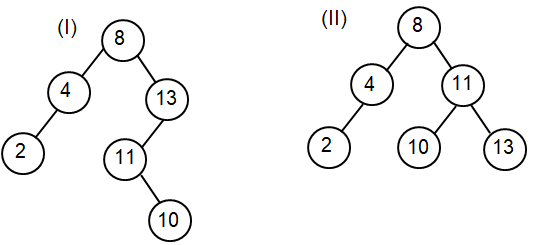
What is an AVL Tree?
Which of the below Figure is following AVL Tree property
Maximum height of a balanced Binary Search tree with n keys
Which of the following is a key factor for preferring B+ trees to BST for indexing db relation?